- 15 Marks
PM – Nov 2024 – L2 – Q7b – Divisional Performance Measurement
Evaluating division performance using ROI and residual income methods with adjusted cost of capital.
Question
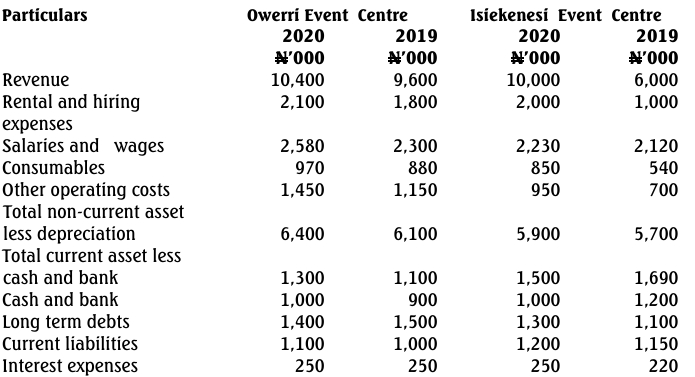
Ngerige and Sons Limited has four operating divisions spread across four cities in Nigeria: Lagos, Kano, Gombe, and Enugu. These divisions are treated as investment centres for performance reporting purposes. The following information is available:
| Particulars | Lagos | Kano | Gombe | Enugu |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Divisional Investment (N) | 10,000,000 | 4,000,000 | 3,000,000 | 7,000,000 |
| Divisional Sales (N) | 53,000,000 | 23,000,000 | 24,600,000 | 29,400,000 |
| Divisional Variable Costs (N) | 50,000,000 | 22,000,000 | 23,400,000 | 27,400,000 |
| Specific Fixed Costs (N) | 1,500,000 | 750,000 | 600,000 | 800,000 |
The company’s annual general fixed cost is N1,300,000, apportioned to divisions based on sales. The cost of capital for Ngerige and Sons Limited is 7.5%. Ignore taxation.
Required:
i. Evaluate the performance of the divisions using the following methods:
- ROI method. (3 Marks)
- Residual Income Method. (3 Marks)
ii. Re-evaluate the residual income situation for the company given an adjusted cost of capital of 10%. (3 Marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
Report an error