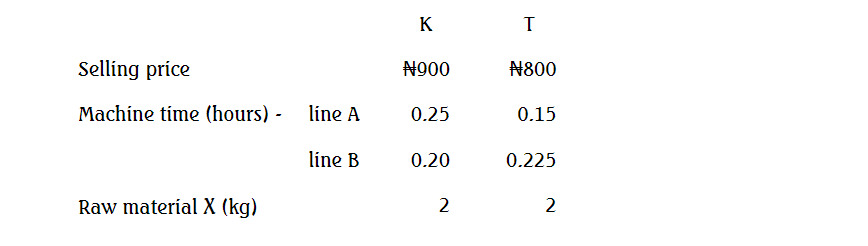
JJ Company specializes in the manufacture and distribution of accessories for cars and motorcycles across central Lagos and the suburbs. The board and management of the company have decided to expand their potential market by capitalizing on the recent demand for pedal cycles caused by congestion and concerns for global warming. They intend to start manufacturing pedal cycles from 2019.
The design team has developed four models A, B, C, and D for the initial launch of the pedal cycle. The manufacturing process involves frame manufacturing and assembly/accessory fitting.
Year 1
At present, there are 40 employees available to undertake frame manufacturing and 20 available for assembly and accessory fitting. Each employee works a 37-hour week, and no overtime is permitted. Employees working on frame manufacturing cost N1,100 per hour, while those working on assembly/accessory fitting cost N1,500 per hour. All employees can be fully utilized elsewhere if not working on this venture.
The anticipated time in hours that each process will take is as follows:
| Model |
Frame Manufacturing (hours) |
Assembly/Accessory Fitting (hours) |
| A |
2.25 |
1.25 |
| B |
2.20 |
1.80 |
| C |
2.20 |
1.40 |
| D |
2.60 |
3.00 |
Direct materials are expected to cost N5,500 for Model A, N6,000 for Models B and C, and N10,000 for Model D. There is no limit on the availability of materials.
Variable overheads of N2,700 per pedal cycle are incurred for both Models A and C, and N3,000 per pedal cycle for both Models B and D.
Fixed overheads allocated to the pedal cycle workshop are N666,000 per annum. The organization uses labor hours to base its overhead absorption rates.
Initial market research indicates that demand and selling prices are likely to be as follows:
| Model |
Number of Pedal Cycles |
Selling Price (N) |
| A |
200 |
14,550 |
| B |
75 |
16,500 |
| C |
220 |
17,000 |
| D |
80 |
24,000 |
Year 2
In Year 2, two additional options are available:
- Lifting the overtime ban and paying overtime at a rate of time and a half. This will necessitate raising the selling price of all units of the specific model being completed outside normal working hours by N2,500 per pedal cycle. The selling price of the other models remains the same as in Year 1.
- Buying in the completed pedal cycle necessary to meet demand from another supplier. This would cost N27,000 per pedal cycle, and the selling price of all units of the model would be increased by N5,500. However, the board is concerned this option may reduce demand.
Required:
a. Determine the production plan that would maximize the profit available to JJ Company in Year 1, assuming no overtime is worked. State the profit that would be earned as a result of this plan. (14 Marks)
b. Advise JJ Company of its most profitable course of action in Year 2, assuming all demand is to be satisfied. (8 Marks)
c. Explain in detail how the relationship between the company and the chosen supplier should be controlled if the directors are considering outsourcing key inputs. (8 Marks)