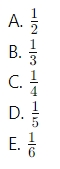- 10 Marks
QTB – May 2017 – L1 – SB – Q4b – Operations Research
Identify non-basic variables in a transportation model and calculate the probability of a specific event in random disk selection.
Question
i. Given the following initial basic tableau of a transportation problem:
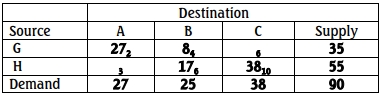
Identify the non-basic variables and compute their corresponding
relative cost coefficients. (4marks)
ii. A bag contains 39,800 white disks and 200 black disks from which
1,000 disks are taken at random. Calculate the probability that the
sample contains 4 black disks. (6marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.