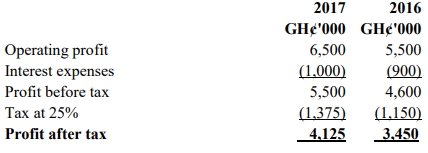- 10 Marks
AT – Nov 2024 – L3 – Q5b – Tax Implications of Foreign Acquisition
Evaluate the tax implications of a 70% equity acquisition by a foreign company and the proposed funding option
Question
Baimbil LTD, based in Australia, has decided to acquire a company in Ghana instead of starting a new one.
The shareholders of Borketey LTD, a resident company in Ghana, have decided to sell the company due to cash flow challenges. As a result, Baimbil LTD approached the management of Borketey LTD and engaged a consultancy firm to perform due diligence checks. Following this, Baimbil LTD acquired 70% of the equity of Borketey LTD.
Below is an extract from the books of Borketey LTD for the 2023 year of assessment:
| Description | Amount (GH¢) |
|---|---|
| Share Capital | 1,000,000 |
| Retained Earnings | (500,000) |
| Shared Deals | 50,000 |
| Bad Debts (Sold to MN LTD, now bankrupt) | 1,000,000 |
Proposed Financing by Baimbil LTD:
The following proposals have been tabled for consideration after the acquisition:
- Baimbil LTD to provide GH¢100 million as debt with 2% interest above the market rate.
- Baimbil LTD to provide GH¢100 million as additional equity capital.
- Baimbil LTD to provide collateral for a bank facility of GH¢100 million in Ghana.
Required:
(i) Evaluate the tax implications of the 70% equity acquisition.
(ii) Evaluate the tax implications of the three proposed financing options.
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.