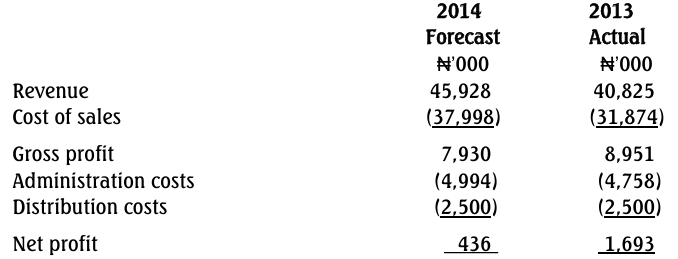- 20 Marks
AA – May 2016 – L2 – Q2 – Planning an Audit
Planning and identifying audit risks for a new client with an increased demand for products, using a standard costing system for inventory valuation.
Question
Sweet Dreams, a limited liability company, is a new audit client and you are at the
planning meeting for the forthcoming audit. The company has grown rapidly and has
May 31 as year-end. The financial statements have not been audited in previous years
since the organization has only just converted from a partnership to a company.
The company’s bankers have requested that an audit be undertaken on the financial
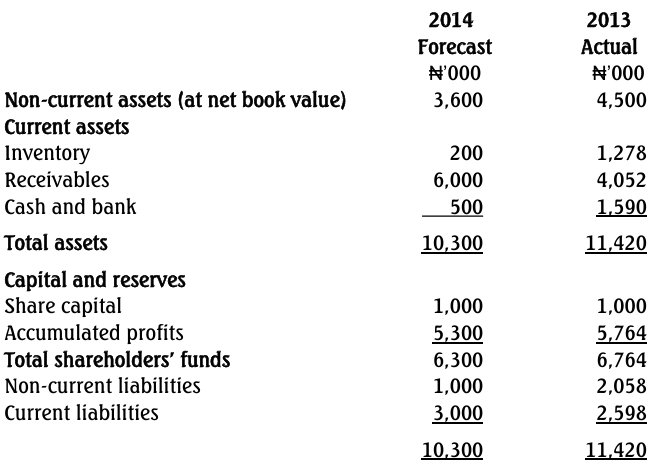
statements for the year ending May 31, 2016. Higher levels of inventory required to
meet the increasing demand for its products have necessitated a request for an increase
in the bank’s overdraft facility.
The company makes beds, buying its materials directly. At the year-end, inventory
comprises raw materials, work-in-progress and finished goods. It does not undertake
continuous inventory counting but does intend to perform a full inventory count on
May 31, 2016. It uses standard costing system to value finished products and work-inprogress.
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
- Tags: Audit Planning, Audit Risk, Control Systems, Inventory Management, Material Misstatement
- Level: Level 2
- Topic: Audit evidence, Planning an Audit, Risk Assessment and Internal Control
- Series: MAY 2016