- 6 Marks
ICMA – Nov 2024 – L1 – Q4b – Day-Rate Incentive Scheme Calculation
Calculates the cost per unit for both low and high day-rate incentive schemes.
Question
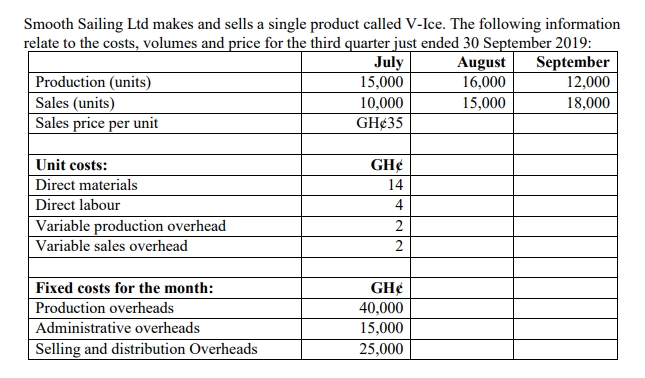
Amanda LTD – Day-Rate Incentive Scheme
Amanda LTD is a manufacturing company and its management is considering the introduction of a high day-rate incentive scheme. During one of such production periods, record shows that, if an employee makes 100 units in a 40-hour week, the employee is paid GH¢2 per hour, but if 120 units are made, the employee is paid GH¢2.50 per hour. Production overhead is added to cost at the rate of GH¢2 per direct labour hour.
Required:
i) What is the cost per unit for the low day-rate scheme?
ii) What is the cost per unit for the high day-rate scheme?
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
- Tags: Cost Calculation, Day Rate Scheme, Incentive Scheme
- Level: Level 1
- Topic: Marginal Costing and Absorption Costing
- Series: Nov 2024