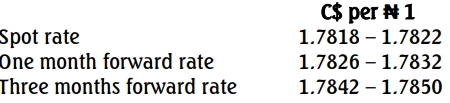- 15 Marks
FM – Nov 2014 – L3 – SC – Q7 – Foreign Exchange Risk Management
Address the calculation of potential exchange rate losses, money market hedging, and the advantages and disadvantages of forward contracts.
Question
-
Build Nigeria Plc. (BNP) is a giant construction company with head office in Kano, Nigeria. It is involved in construction of roads, dams, airfields, etc., in many parts of the country. Recently, the company won construction contracts across a number of African countries. One of the contracts is for the construction of a dam for a country in Central Africa whose currency is Central African Dollar (C$). The dam has now been completed, and the retention money of C$210,000,000 is due for settlement in one year’s time.
The current spot exchange rate is C$40 = N1. Risk-free rate is 5% in Nigeria and 25% in the foreign country.
The Chief Finance Officer (CFO) of BNP is worried about the above financial statistics and concluded that BNP will lose as much as N840,000 due to exchange rate movements between now and the end of the year when the retention money is received.Required:
Explain, showing all relevant calculations, how the CFO arrived at the potential loss of N840,000. (4 Marks)b. In another contract in a country in the ECOWAS sub-region (with currency of W$), BNP expects the following payment and receipt in six months’ time:
You are provided with the following financial data:- Spot exchange rate:
N per W$1 = 1.4735 – 1.4755 - Money Market Rates:
Deposit % Borrowing % Nigeria 13.25 West African Country 6.5
Required:
Show how BNP can make use of money market hedge to mitigate the foreign exchange risk inherent in the above payment and receipt. Show all workings and the necessary steps.(7 Marks)
c. Discuss TWO advantages and TWO disadvantages of forward exchange contracts.
(4 Marks)
- Spot exchange rate:
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.