- 20 Marks
PM – Nov 2014 – L2 – Q2 – Standard Costing and Variance Analysis
Calculate various cost and sales variances, including an operating statement for Ibek Limited.
Question
Ibek Limited manufactures a standard product and operates a system of variance accounting using a fixed budget.
As a newly appointed Management Accountant, you are responsible for preparing the monthly operating statements.
Extracts from the budget for the standard product cost and actual data for the month ended 31 December 2013 are given below:
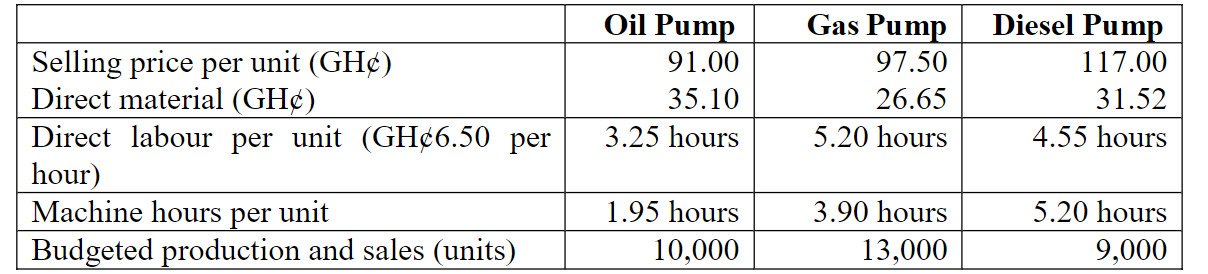
Budgeted and Standard Cost Data:
- Budgeted sales and production for the month: 20,000 units
- Standard cost for each unit of product:
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Direct materials: | A: 10 kg at N2 per kg |
| B: 5 kg at N10 per kg | |
| Direct wages | 5 hours at N6 per hour |
| Fixed overhead | Absorbed at 200% of direct wages |
- Budgeted sales price has been calculated to give a margin of 20% of sales price.
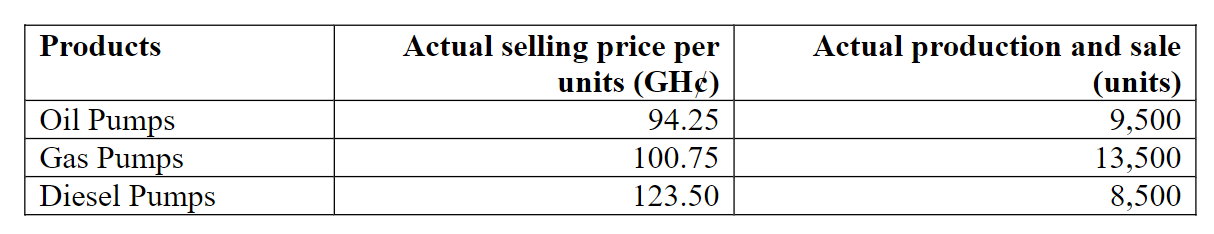
Actual Data for the Month Ended 31 December 2013:
- Production: 19,000 units sold at a price of 15% higher than that budgeted
- Direct materials consumed:
| Item | Quantity | Cost per kg |
|---|---|---|
| Material A | 192,000 kg | N2.40 |
| Material B | 96,000 kg | N9.40 |
- Direct wages incurred: 92,000 hours at N6.40 per hour
- Fixed production overhead incurred: N580,000
Required:
(a) Prepare the operating statement for the month ended 31 December 2013. (3 Marks)
(b) Calculate the following variances: i. Direct material cost variance (5 Marks)
ii. Direct labour variances (5 Marks)
iii. Overhead variances (3 Marks)
iv. Sales variances (4 Marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.