- 20 Marks
FR – Nov 2024 – L2 – Q3 – Financial Statements Preparation
Preparation of Fahnbulleh LTD’s Statement of Comprehensive Income and Statement of Financial Position using IFRS.
Question
Fahnbulleh LTD (Fahnbulleh) is a well-known company manufacturing thrill rides. During the current economic climate, Fahnbulleh has experienced some difficulties and has had to close down its Merry Go Round division.
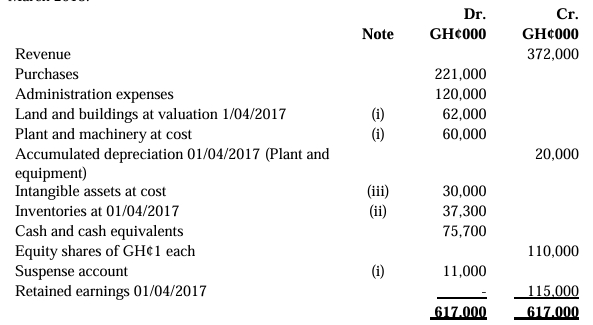
The company’s trial balance as at 31 October 2023 is as follows:
| Account Description | Dr (GH¢’000) | Cr (GH¢’000) |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue | 1,296,000 | |
| Cost of Sales | 546,480 | |
| Distribution Costs | 127,080 | |
| Administrative Expenses | 142,560 | |
| Investment Income | 28,080 | |
| Investment Property | 270,000 | |
| Interest Paid | 17,280 | |
| Income Tax | 10,800 | |
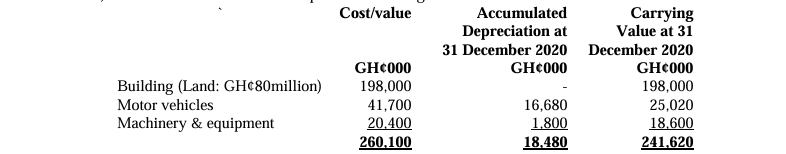
| Property, Plant & Equipment (PPE) – Carrying Value at 1 Nov 2022 | 1,620,000 | |
| Inventories (31 October 2023) | 108,000 | |
| Trade Receivables | 135,000 | |
| Bank | 64,800 | |
| Payables | 43,200 | |
| Deferred Tax (1 Nov 2022) | 75,600 | |
| 8% Loan Note | 432,000 | |
| Ordinary Share Capital (GH¢1 per share) | 540,000 | |
| Retained Earnings (1 Nov 2022) | 605,520 | |
| Totals | 3,031,200 | 3,031,200 |
Additional Information:
-
Revenue Adjustments:
- Revenue includes VAT of GH¢72 million.
-
Property, Plant & Equipment (PPE):
- A building with a carrying value of GH¢54 million was revalued on 1 November 2022 to GH¢72 million.
- The building had an estimated useful life of 25 years when purchased, and this has not changed after the revaluation.
- All other PPE should be depreciated at 20% per annum (reducing balance method).
- All depreciation should be charged to cost of sales.
-
Closure of the Merry Go Round Division (Discontinued Operations):
- Closure Date: 1 October 2023
- Division’s Results (1 Nov 2022 – 1 Oct 2023):
Item GH¢’000 Revenue 58,800 Cost of Sales 38,700 Distribution Costs 12,240 Administrative Expenses 11,880 - The division’s net assets were sold at a loss of GH¢19.2 million, recorded in cost of sales.
-
Investment Property Revaluation (IAS 40):
- Investment property value increased by 5%, which should be incorporated into the financial statements.
-
Income Tax and Deferred Tax (IAS 12):
- The estimated income tax provision for the year: GH¢140.4 million.
- Deferred tax liability should be adjusted for temporary differences (GH¢129.6 million) at a 25% tax rate.
-
Damaged Inventory (IAS 2):
- Inventory worth GH¢46 million was damaged.
- It can be reconditioned at a cost of GH¢12 million and sold for GH¢52 million.
- Appropriate adjustments should be made.
Required:
Prepare and present the Statement of Comprehensive Income for the year ended 31 October 2023 and the Statement of Financial Position as at 31 October 2023 for Fahnbulleh LTD.
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.