- 15 Marks
MI – Nov 2021 – L1 – SB – Q1a – Costing Methods
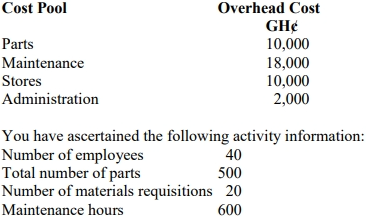
Calculate overhead absorption rate per unit based on labour hours.
Question
ABCD is into manufacturing of two products, AB and CD, using similar equipment and methods. The following data were collected from the company’s record:
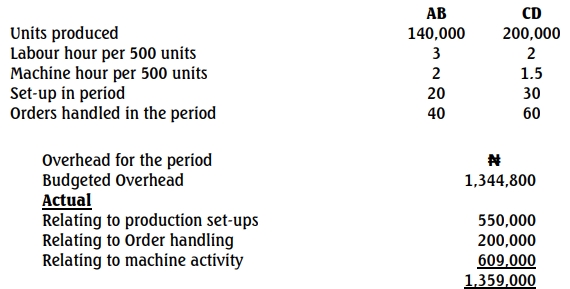
Calculate the overheads to be absorbed per unit of each product based on
i. Conventional absorption costing using predetermined labour hour
absorption rate. (6 Marks)
ii. An ABC approach using suitable cost drivers. (9 Marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
- Tags: Costing, Labour Hour Rate, Overhead Absorption
- Level: Level 1
- Topic: Costing Methods
- Series: NOV 2021