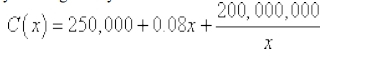- 30 Marks
PM – Nov 2016 – L2 – Q1 – Decision Making Techniques
Evaluate profit maximization, machine bottlenecks, and inventory valuation using marginal and throughput accounting approaches.
Question
Hicenta Limited makes three products Soyi, Milco and Yoghurt. All the three
products must be offered for sale each month in order to provide a complete
market service. The products are fragile and their quality deteriorates rapidly
shortly after production.
The products are produced on two types of machine and worked on by a single
grade of direct labour. Fifty direct employees are paid N80 per hour for a
guaranteed minimum of 160 hours per month.
All the products are first pasteurised on a machine type A and then finished
and sealed on a machine type B.
The machine hour requirements for each of the products are as follows:
Machine Information:
| Machine Type | Product | Hours per Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Machine A | Soyi | 1.5 |
| Machine A | Milco | 4.5 |
| Machine A | Yoghurt | 3.0 |
| Machine B | Soyi | 1.0 |
| Machine B | Milco | 2.5 |
| Machine B | Yoghurt | 2.0 |
The capacity of the available machines type A and B are 6,000 hours and 5,000
hours per month respectively. Details of the selling prices, unit costs and
monthly demand for the three products are as follows:
Product Costs and Demand:
| Product | Selling Price (N per unit) | Concentrate Cost (N per unit) | Other Direct Material Cost (N per unit) | Direct Labour Cost (N per unit) | Overheads (N per unit) | Profit (N per unit) | Maximum Monthly Demand (units) |
| Soyi | 910 | 220 | 230 | 60 | 240 | 160 | 1,200 |
| Milco | 1,740 | 190 | 110 | 480 | 620 | 340 | 700 |
| Yoghurt | 1,400 | 160 | 140 | 360 | 520 | 220 | 600 |
Although, Hicenta Limited uses marginal costing and contribution analysis as
the basis for its decision making activities, profits are reported in the monthly
management accounts using the absorption costing basis. Finished goods
inventories are valued in the monthly management accounts at full absorption
cost.
You are required to:
a. Calculate the monthly machine utilisation rate for each product and
explain which of the machines is the bottleneck/limiting factor.
(6 Marks)
b. Use current system of marginal costing and contribution analysis to
calculate the profit maximising monthly output of the three products.
(6 Marks)
c. Explain why throughput accounting might provide more relevant
information in Hicenta‟s circumstances. (6 Marks)
d. Use a throughput approach to calculate the throughput-maximising
monthly output of the three products. (6 Marks)
e. Explain the throughput accounting approach to optimizing the level of
inventory and its valuation. Contrast this approach to the current system
employed by Hicenta. (6 Marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.