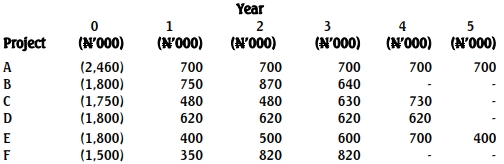
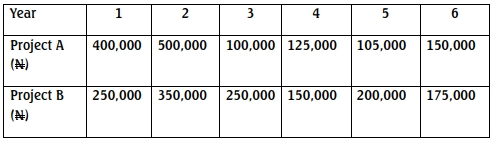
- 20 Marks
FM – Nov 2024 – L2 – Q2 – Investment Appraisal
Calculate the NPV of launching two new products, Agbui and Loloi, and advise on the investment decision.
Question
Santrofi PLC is a publisher that wants to expand its market share in magazine publications. The company plans to launch two new products, Agbui and Loloi, at the start of January 2025, which it believes will each have a 4-year life span. The sales mix is assumed to be fixed. The information below is relevant:
- Expected sales volumes (units) for Agbui:
| Year | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume | 30,000 | 55,000 | 50,000 | 15,000 |
-
The first year’s selling price and direct material costs for each Agbui unit will be GH¢31 and GH¢12, respectively. On the other hand, the company expects to sell 25% more Loloi units than Agbui. Both selling price and direct material cost of Loloi are expected to be 25% less than Agbui’s.
-
Incremental fixed production costs are expected to be GH¢500,000 in the first year of operation, apportioned based on revenue. Advertising costs will be GH¢250,000 in the first year of operation and then GH¢125,000 per year for the following two years.
-
To produce the two products, an investment of GH¢1 million in machinery and GH¢500,000 in working capital will be needed, payable at the start of the period. Santrofi PLC expects to recover GH¢600,000 from the sale of machinery at the end of the project life. Investment in machinery attracts a 100% first-year tax-allowable depreciation. The company has sufficient profit to take full advantage of the allowance in Year 1. For the purpose of reporting accounting profit, the company depreciates machinery on a four-year straight-line basis.
-
Revenue and costs are expected to be affected by inflation after the first year as follows:
- Selling price: 3% a year
- Direct material cost: 3% a year
- Fixed production cost: 5% a year
-
The company’s real discount rate is 10% for investment appraisal. Average inflation is deemed to be 3%. The applicable corporate tax rate is 25%.
Required:
Calculate the Net Present Value (NPV) of the proposed investment in the two products and advise the company on its investment appraisal.
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.