- 30 Marks
PM – May 2017 – L2 – SA – Q1 – Working Capital Management
Calculate KPIs for Kardex’s products, perform a PEST analysis, and comment on KPI effectiveness in external conditions.
Question
- Kardex Industries Nigeria Limited is a subsidiary of a large manufacturing company based in China (Kardex International). The company manufactures washing machines, table gas cookers, and refrigerators which are being sold by the subsidiary in Nigeria. Demand for the company’s product is growing, especially among the growing middle-class population, until recently when the company started experiencing some hiccups due to the economic recession and stiff competition.
- The company currently sells two types of washing machines in Nigeria:
- Wash Up: A basic product comparable to local competitors.
- Perfect Wash: A premium product similar to Kardex’s offerings in developed countries.
- The competitive environment in Nigeria is evolving quickly. Apart from Kardex, two other companies offer similar machines in the market. One competitor produces machines similar to “Wash Up” locally with tax incentives, while the other is planning to set up a plant for specialized washing machines akin to Kardex’s “Perfect Wash.”
- Kardex International’s mission is to be the “industry leader.” The Kardex Board has identified critical success factors (CSFs) for the Nigerian subsidiary:
- Market leadership.
- Profit maximization and shareholder wealth within acceptable risk.
- Brand image maintenance as a top-of-the-range product.
- The Board suggests using the following KPIs for each product:
- Total profit, average sales price per unit, contribution per unit, market share, margin of safety, return on capital employed (ROCE), and total quality costs.
- The company currently sells two types of washing machines in Nigeria:
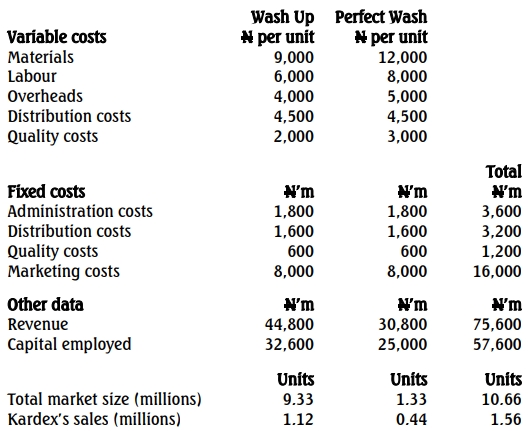
Appendix 1
Financial Year Data for Nigerian Subsidiary:
Requirements:
a. Calculate the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Kardex, including:
- Total Profit
- Average Sales Price per Unit
- Contribution per Unit
- Market Share
- Margin of Safety
- Return on Capital Employed (ROCE)
- Quality Costs (20 Marks)
b. Use a PEST Analysis to identify external environmental issues affecting Kardex and discuss the effectiveness of the KPIs in addressing these issues.
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
- Tags: KPI, Margin of Safety, Market Share, Profitability analysis, Quality Costs, ROCE
- Level: Level 2
- Topic: Working Capital Management
- Series: MAY 2017

