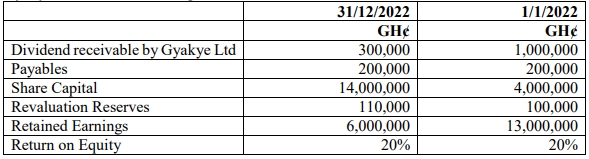
- 5 Marks
AAA – Nov 2024 – L3 – Q2b – Audit Procedures for Long-term Loan in Ecowud Co. LTD
Audit procedures to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence for a long-term loan.
Question
Ecowud Co. LTD (Ecowud) is a sustainable goal-oriented company that develops, manufactures, and sells plywood made from rice husk and plastic waste. The company operates across Ghana and West Africa and has secured a GH¢3.5 million long-term loan as part of its financial restructuring. The loan agreement has bank-imposed financial conditions, including maintaining a minimum total asset level. If these conditions are breached, the loan becomes immediately repayable.
As part of the audit procedures, you are required to obtain sufficient and appropriate audit evidence regarding the GH¢3.5 million long-term loan.
Required:
Describe FIVE audit procedures you would perform to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence in relation to the long-term loan of GH¢3.5 million.
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
- Tags: Audit evidence, Compliance, Debt Classification, Financial Statements, Loan
- Level: Level 3
- Topic: Audit evidence, Loan Compliance
- Series: Nov 2024