- 20 Marks
PM – Nov 2016 – Q2 – Cost Management Strategies
Question requires explanation of Life Cycle Costing concepts and calculation of unit costs over 3-year product lifecycle for a CD manufacturer.
Question
Tadesco Limited manufactures Compact Disks. It is planning to introduce a new model and production will begin very soon. It expects the new product to have a life cycle of three years and the following costs have been estimated.
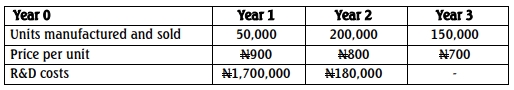
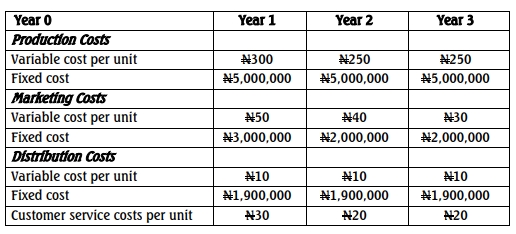
You are required to:
a. Explain Life Cycle Costing and state what distinguishes it from traditional costing technique. (10 Marks)
b. Calculate the cost per unit over the whole life cycle and comment on the price to be charged. (10 Marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.

