- 15 Marks
May 2023 – L2 – SA – Q7 – Pricing Decisions
Calculation of minimum price Kola Plc should quote for 400 units of special security padlock keys using learning curve principles.
Question
Kola Plc produces and sells a brand of security padlock keys. Its budget for next year is as follows:
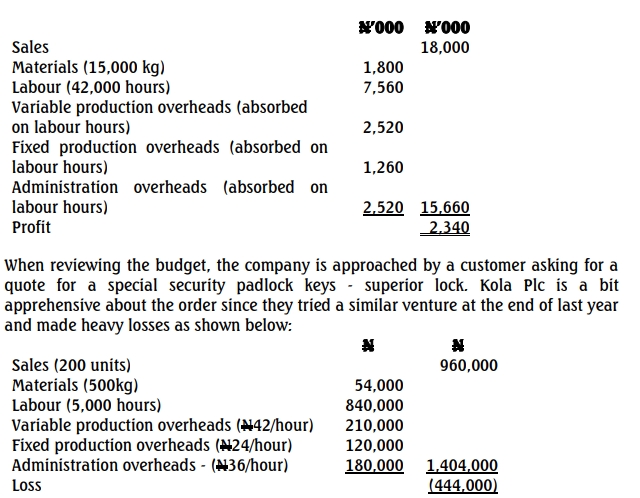
Further research showed that the time taken for the first 50 units was 1,800 hours and the first 100 units took 3,000 hours. The customer is insistent that Kola Plc at least quotes a price for his requirement of 400 units.
Kola Plc is reluctant because the order would divert labour away from the regular padlock keys, and they cannot recruit more staff. If the contract is taken on, the same material would be used, with fixed production overheads of N150,000 and N30,000 administration costs.
Required:
Calculate the minimum price Kola Plc should quote for the 400 units of the special padlock keys.
(Total 15 Marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
- Tags: Fixed Costs, Learning Curve, Special Order Pricing, Variable Costs
- Level: Level 2
- Topic: Pricing Decisions
- Series: MAY 2023

