- 30 Marks
CR – May 2022 – L3 – Q1 – Leases (IFRS 16)
Adjust lease accounting for right-of-use asset and lease liability in compliance with IFRS 16.
Question
The draft financial statements of Gbola Limited group and its investee companies Tanko Limited and Eze Limited at December 31, 2018 are shown below:
Draft Statements of Profit or Loss for the Year Ended December 31, 2018
| Item | Gbola Limited (N’000) | Tanko Limited (N’000) | Eze Limited (N’000) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | 17,070 | 7,320 | 2,235 |
| Cost of Sales | (8,640) | (3,210) | (885) |
| Gross Profit | 8,430 | 4,110 | 1,350 |
| Other Operating Expenses | (2,070) | (810) | (600) |
| Profit from Operations | 6,360 | 3,300 | 750 |
| Interest Expense | (570) | (660) | (210) |
| Profit Before Tax | 5,790 | 2,640 | 540 |
| Income Tax Expense | (810) | (360) | (90) |
| Profit for the Year | 4,980 | 2,280 | 450 |
Draft Statements of Financial Position as at December 31, 2018
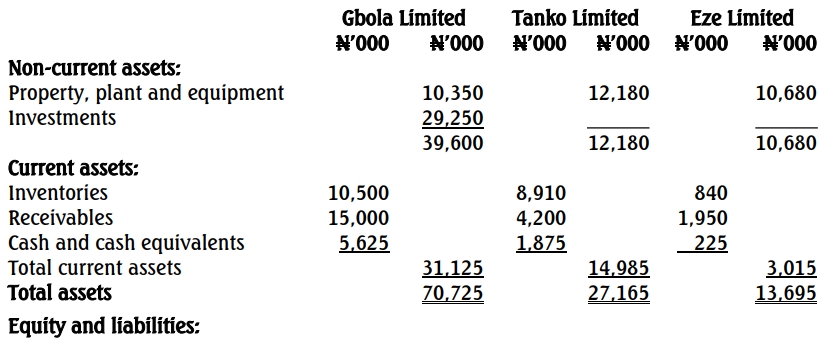
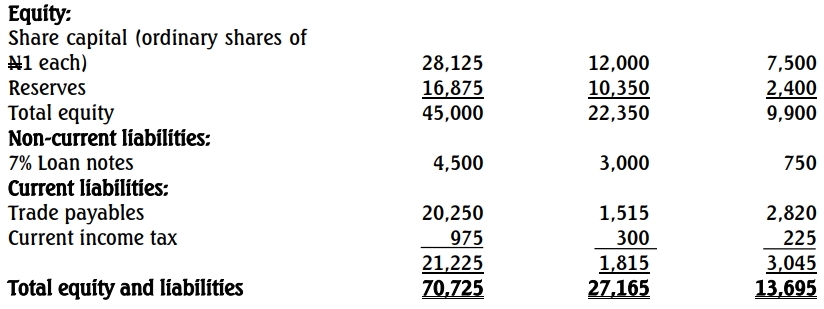
Additional Information
- On January 1, 2014, Gbola Limited acquired 9,000,000 ordinary shares in Tanko Limited for N23,250,000 when the reserves of Tanko Limited were N3,000,000.
- A new asset with a fair value of N1,500,000 was acquired during the year under a lease agreement by Gbola Limited. A clause in the lease agreement stipulated that N300,000 payments must be paid on December 31, each year for six years, starting from December 31, 2018. The interest rate implicit in the lease is 5.47%. Gbola Limited treated this as an operating expense; because the only accounting entry that the company believes must be made in relation to this asset is the N300,000 payment it has made.
- Gbola Limited had an intangible asset of N750,000 for software in its statement of financial position. The directors of Gbola Limited believed that the software will have no recoverable value at the date of acquisition, and Tanko Limited wrote it off shortly after its acquisition.
- At the date of acquisition of Tanko Limited, the carrying amount of its property, plant, and equipment, considered to have a remaining life of 10 years, was N5,625,000 lower than its fair value.
- On January 1, 2017, Gbola Limited acquired 2,250,000 ordinary shares in Eze Limited for N6,000,000 when the reserves of Eze Limited were N1,350,000. The carrying amount of assets of Eze Limited was the same as their fair values at that date. Depreciation should be treated as an operating expense.
- A component used by both Tanko Limited and Eze Limited is produced by Gbola Limited, and it sells this component at a margin of 25%. Goods worth N780,000 were sold to Tanko Limited during the year. None of these goods had been sold by Tanko Limited at December 31, 2018. Gbola Limited also sold goods worth N1,200,000 to Eze Limited, and Eze Limited sold all of these goods as at December 31, 2018.
- N900,000 in respect of amounts owed by Tanko Limited and N525,000 in respect of amounts owed by Eze Limited were included in the receivables of Gbola Limited. The corresponding balances in Tanko Limited and Eze Limited payables were N600,000 and N525,000, respectively. On December 31, 2018, Tanko Limited sent a cheque of N300,000 to Gbola Limited.
- There has been no impairment for Eze Limited. However, the impairment test conducted on Tanko Limited’s goodwill showed that goodwill is being impaired by 10% per annum on a straight-line basis.
- Gbola Limited’s cash and cash equivalents included a Director’s loan of N1,500,000. The Directors are of the view that the inclusion does not contravene any International Financial Reporting Standard.
- The goodwill arising on the acquisition of Tanko Limited is being amortized over a 10-year period, though this practice contravenes IAS 36, which prohibits goodwill amortization and instead requires annual impairment tests.
a. Prepare the necessary adjustments to account for the lease contract based on additional information provided in (ii) above in accordance with IFRS 16. (5 Marks)
b. Prepare the consolidated statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income for the group for the year ended December 31, 2018. (8 Marks)
c. Prepare the consolidated statement of financial position of Gbola Limited group as at December 31, 2018. (12 Marks)
d. Discuss the ethical implication of the Director’s action in note (ix) above. (5 Marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
- Tags: Depreciation, IFRS 16 Adjustments, Interest expense, Lease Liability, Right-of-Use Asset
- Level: Level 3
- Topic: Leases (IFRS 16)

