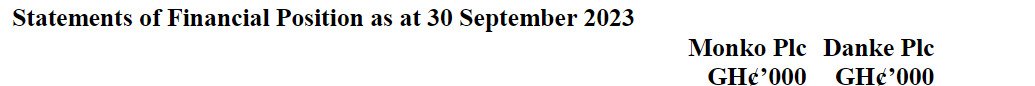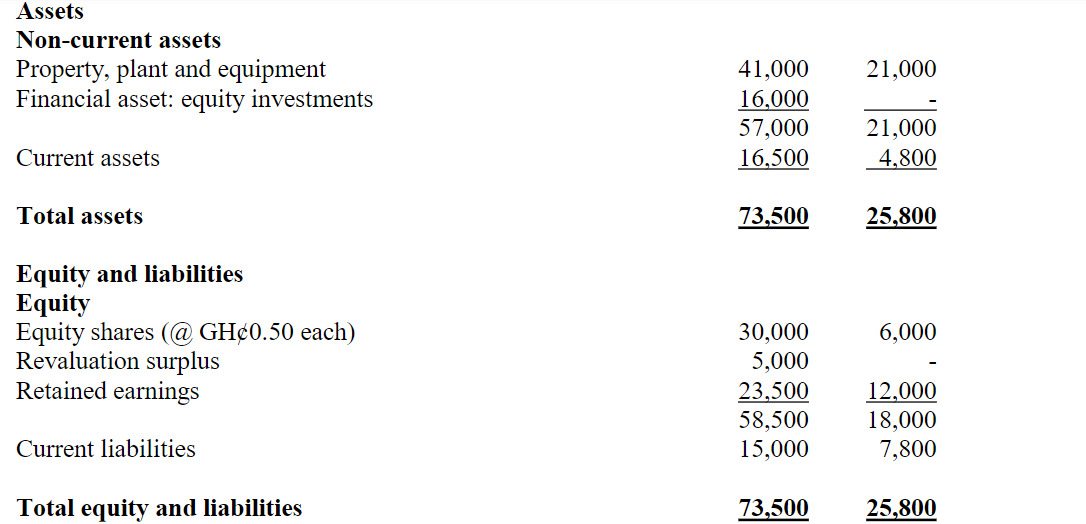- 5 Marks
FR – Nov 2022 – L2 – Q3b – Bargain Purchase and IFRS 3 Review Requirements
Explanation of a bargain purchase and IFRS 3 items requiring review when gain from bargain purchase arises.
Question
b. A gain from a bargain purchase may arise in the course of a business combination and when this happens, the acquirer must review or reassessthe procedure used to measure certain items at the acquisition date.
Required:
Explain the term “Gain from a bargain purchase” and identify the three
items stipulated in IFRS 3 that must be reviewed.
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
- Tags: Acquisition Date, Bargain Purchase, IFRS 3, Negative Goodwill, Reassessment
- Level: Level 2
- Topic: Business Combinations (IFRS 3)
- Series: NOV 2022