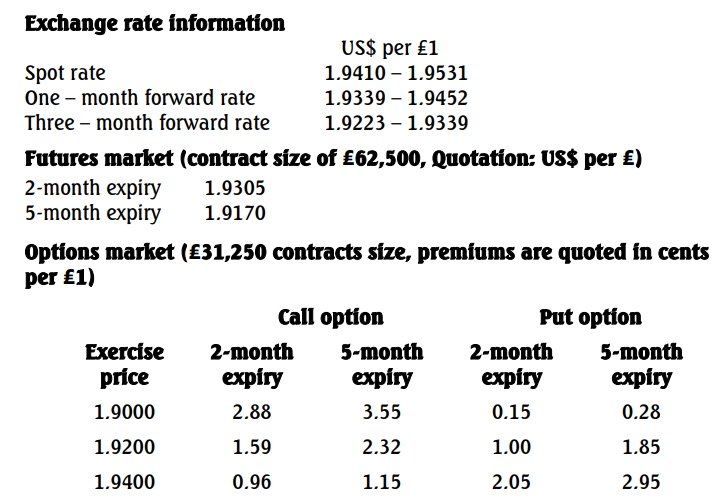
- 10 Marks
SCS – Nov 2024 – L3 – Q4c – Forward Rate Agreement for Interest Rate Risk Management
Calculation of settlement amount for FRA under different Ghana Reference Rate (GRR) scenarios.
Question
The company has decided to use a Forward Rate Agreement (FRA) to manage its interest rate risk likely to arise from the short-term loan of GH¢15 million it intends to borrow in three months for a period of six months.
Required:
i) What is the purpose for a company to enter into an FRA arrangement? (2 marks)
ii) Calculate the amount of money that will be paid to settle the FRA at the beginning of the FRA period if, at the end of month 3, when the FRA becomes effective, the six-month Ghana Reference Rate (GRR) is as follows:
a) 37.50%
b) 28.50%
In each case, clearly state the party (i.e. FRA buyer or FRA seller) responsible for making the payment.
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.