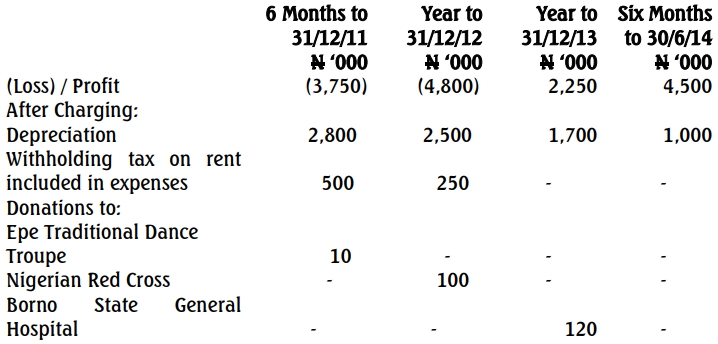
- 8 Marks
FM – May 2016 – L3 – Q6b – Investment Appraisal Techniques
Calculating the betas, required rates of return, and stock prices for three securities based on market data and forecasts.
Question
The expected return on the market portfolio (estimated from past data) is 12% p.a. with a standard deviation of 15% and the risk-free rate of 4% p.a. The actual prices, last year dividends, and the covariances from three securities (A, B, C) with the market are given in the table below:
| Security | Actual Price (N) | Last Year Dividend (N) | Covariance with Market |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 107 | 1.30 | 0.025650 |
| B | 618 | 18.00 | 0.018675 |
| C | 1,350 | 22.00 | 0.029025 |
You are required to:
i.
Calculate the betas and the required rates of return of securities A, B, and C. (3 Marks)
ii.
In the table below, you have the market consensus forecast of 12-month price targets, ex-dividends, and the expected dividend growth rate of the securities.
| Security | 12-month price target (N) | Dividend growth rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 122.50 | 12 |
| B | 740.00 | 10 |
| C | 1,500.00 | 11 |
Assuming the dividends are paid in 12 months exactly, compute the required stock price for the 3 stocks and state your conclusion. (4 Marks)
iii.
Considering the results in (ii) above, explain briefly what will be your strategy? (1 Mark)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
- Tags: Beta, CAPM, Dividends, Market Portfolio, Required Return, Stock valuation
- Level: Level 3