- 12 Marks
FM – May 2022 – L3 – Q6a – Foreign Exchange Risk Management
Evaluate hedging methods for a UK supplier payment of £5 million in three months.
Question
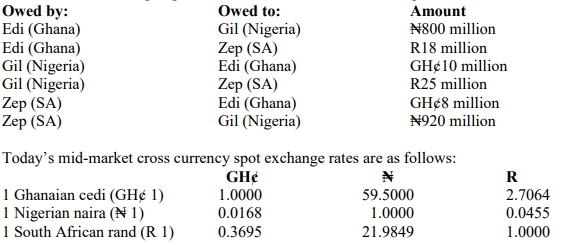
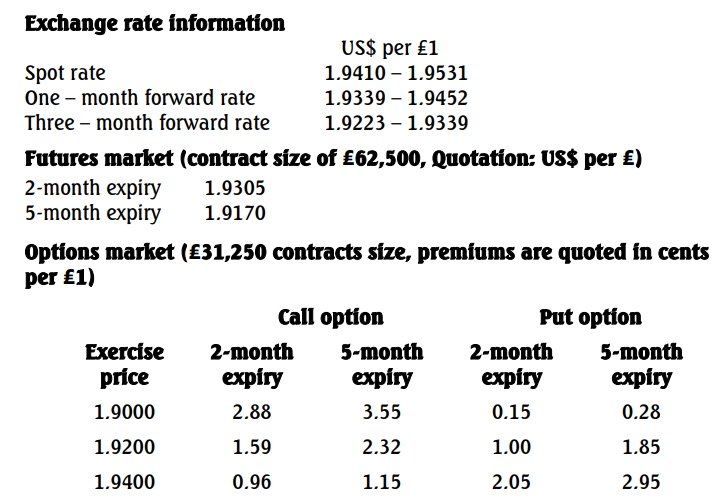
a. You have worked with a major oil servicing company in Nigeria, with headquarters in the USA, for the past six years. Recently you completed your ICAN examinations, and you have been asked to join the international treasury department in New York City for a two-year attachment. The company is due to pay a UK supplier the sum of ₤5million in three months’ time. Your team is considering alternative methods of hedging the expected payment against adverse movements in exchange rate.
You are required to advise the company which of the following hedging strategies should be adopted for the payment due to be made in three months. Show all workings:
i. Forward contract (2 Marks)
ii. Currency futures (5 Marks)
iii. Currency options (5 Marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.
- Tags: Currency Futures, Currency options, Forward Contracts, Hedging
- Level: Level 3