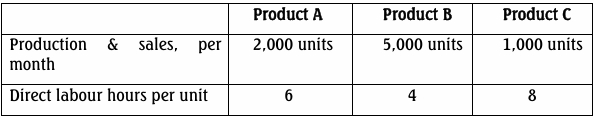
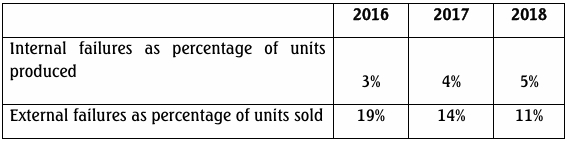
- 5 Marks
SCS – Nov 2024 – L3 – Q2b – Integration/Responsiveness Matrix and Cost Reduction
Advising BOGML’s MD on the best international strategies under the IR Matrix to achieve cost reduction in expansion.
Question
The Board of BOGML has approved the Managing Director’s proposal to expand operations into Tanzania and South Africa by 2026. A key strategic focus of the company has been cost reduction, due to the narrow profit margins prevalent in the industry.
Required:
Using the Integration/Responsiveness (IR) Matrix, advise Dr. Ayimadu Baffour on the two most suitable international strategies/choices that have a low requirement for local responsiveness but can effectively support his cost reduction objectives. Clearly identify and explain the two strategies within the IR Matrix that prioritize cost reduction.
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.