- 1 Marks
MI – May 2017 – L1 – SA – Q10 – Costing Techniques
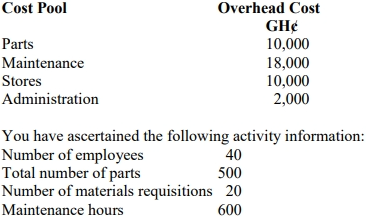
Identify incorrect cost pool to cost driver relationship.
Question
Which of the following cost pools to cost drivers relationship is incorrect?
A. Set-up to number of set-ups
B. Material handling to number of material movement
C. Maintenance to number of maintenance
D. Depreciation of machine to number of machine hours
E. Material procurement to number of inspection
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.