- 30 Marks
PM – Nov 2024 – L2 – Q1 – Decision-Making Techniques
Optimization of Oshimiri Nigeria Limited's production plan to maximize profits under resource constraints using linear programming.
Question
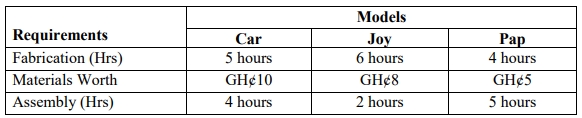
Oshimiri Nigeria Limited, a company based in Aba, produces two grades of industrial vanish. The selling price and associated unit variable costs for vanish Grade A and Grade B are shown below:
| Particulars | Grade A | Grade B |
|---|---|---|
| Selling Price | N2,100 | N1,500 |
| Material X (N240/kg) | N480 | N240 |
| Skilled Labour (N144/hr) | N720 | N288 |
| Unskilled Labour (N60/hr) | N120 | N180 |
| Variable Overhead (N84/machine hr) | N168 | N336 |
The fixed overhead costs are N2,600,000 per month. The company plans to maximize profits.
The availability of resources for the following month is as follows:
- Material X: 25,000 Kg
- Skilled Labour: 48,000 hours
- Unskilled Labour: 39,000 hours
- Machine hours: 50,000 hours
Required:
a. Identify the objective function and the constraints of the model to be used in determining the optimum production plan for the following month. (5 Marks)
b. Determine the optimum production plan for the month and the associated profit. (5 Marks)
c. Explain the concept and significance of dual prices and slack variables in the context of the model used by the company in this scenario. (4 Marks)
d. Calculate the dual prices for constraints identified in this scenario. (10 Marks)
e. Suggest ways in which the management can overcome the capacity constraints identified above during the month and the cost implications. (6 Marks)
Find Related Questions by Tags, levels, etc.