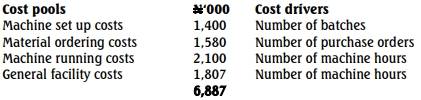
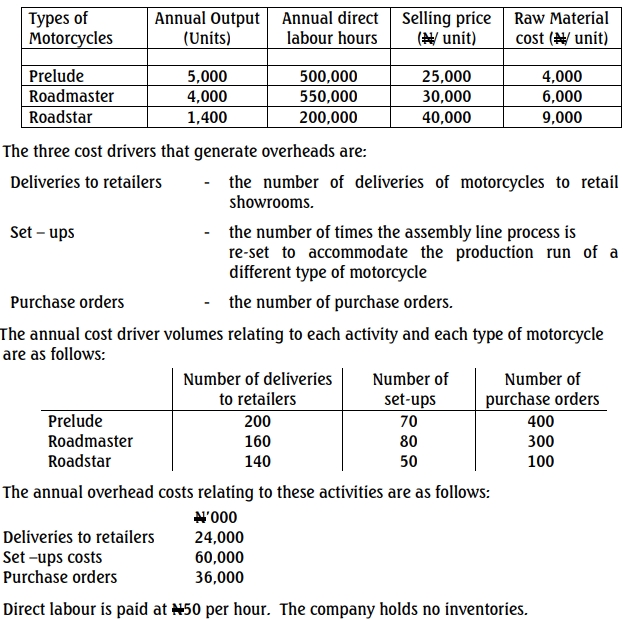
Adelab Nigeria Limited is a manufacturer of industrial gear. Over the years, the company has collected, allocated and absorbed overhead cost based on the traditional absorption costing technique.
The current economic recession in the country and stiff competition in the market are seriously affecting the company’s performance and market share as its competitors have in recent times, introduced discounts to their customers. The customers of Adelab have therefore been putting pressure on the company to follow suit and few of these customers have started patronising the company’s competitors who offer discounts on every purchase.
To address these problems and other strategic and operational issues affecting the company, the Board of Directors of Adelab decided recently to appoint a seasoned management expert as Business Process Executive (BPE). The BPE recently advised the Board to organise a management retreat. The focus of the retreat is strategic management, cost control and performance management. During the course of the retreat, new costing techniques such as activity based management, life cycle costing, target costing, Kaizen costing, throughput accounting, backflush accounting, just in time approach to inventory management, etc., were discussed by the BPE. The need to also consider both financial and non-financial performance measurements was also discussed. The BPE further highlighted the need for the company to link its Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to its strategic and operational Critical Success Factors (CSF), to achieve a better focus and improve its financial performance.
In a board meeting after the retreat, the following discussions took place:
Technical Director: “To improve our financial performance I think I will have to agree
with the BPE‟s submission at the retreat that we replace absorption costing approach
with an Activity Based Costing (ABC) system. I believe this will help us to put a tap on
cost and thus improve cost control and increase profit margins. We can then pass
some of these costs reduction to our customers in form of discounts”.
Managing Director: “Yes, I agree with your opinion but I also think we need to
monitor our performance in both financial and non-financial terms. For example, loss
of sales could be due to charging a higher price than our competitors and as well as
producing bad quality product. I therefore think that, while we should consider
introducing activity based costing, we should also consider ways in which the
company could monitor and assess performance on a wider basis”.
You are required to:
a. Describe FIVE key features of Activity Based Costing (ABC) and provide SIX advantages and FOUR disadvantages of adopting Activity Based Costing (ABC) approach to cost accumulation. (10 Marks)
b. Explain the need for the measurement of organisational and managerial performance giving examples of the range of financial and non-financial performance measures that might be used. (10 Marks)